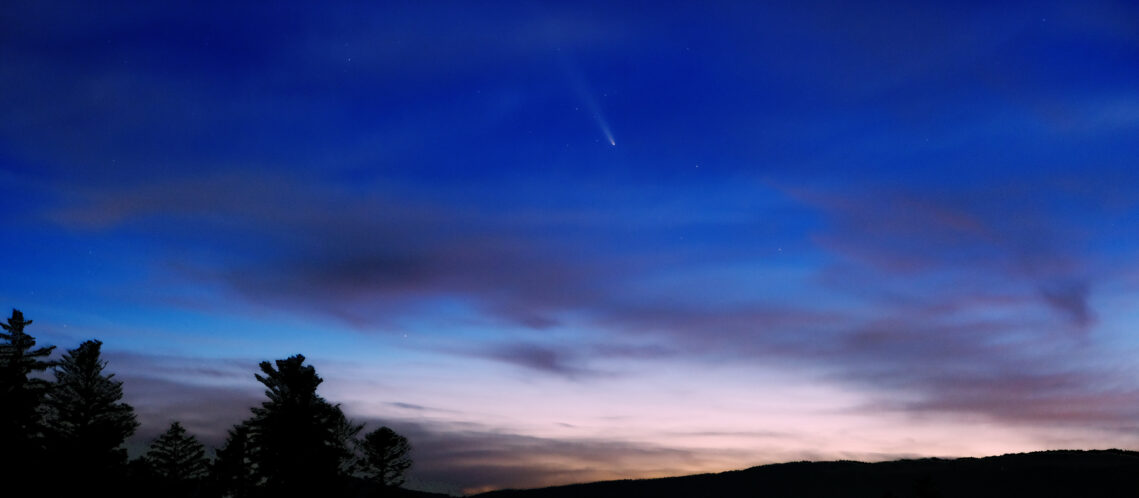
I have been following this new stargazer comet since the end of September. It was kind of a gamble to know if this comet would survive passing so close to the sun and survive. But thankfully, it did survive and what a spectacle it is giving us. It might not be as bright as Neowise in 2020, but this time, I have a better camera to capture it and the pictures are just amazing. Too bad the weather was so cloudy this week… These pictures and videos were taken with my Fujifilm XT4, with the 18-55 mm or the 50-140 …
Tsuchinshan–ATLAS comet photos album