This year at the AKL Conference was prominently marked by discussions on Artificial Intelligence (AI). The rapid advancements in AI, significantly propelled by platforms like OpenAI and ChatGPT, have captured the attention of key decision-makers in leading companies such as Trumpf and Coherent. The plenary talk particularly emphasized the potential applications, implications, and the urgent need for Europe to act before falling behind. The debate highlighted concerns about the United States and China leading the way, while the European Union lags due to stringent regulations. A recurrent theme was the term “cyberphotonic,” which seems to blend photonics and virtualization, involving …
Category: Optics
Methods for Cleaning Optics in the Lab and Industry
This post aims to provide comprehensive guidance on cleaning optical elements. While there is a wealth of information available online, particularly on suppliers’ websites, I want to consolidate all the knowledge I’ve acquired over the years working with lasers, fiber optics, and other optical equipment, including some tips and tricks. How to Clean an Optical Element Identifying the Optical Surface Is it a lens, a mirror, a filter, etc.? Optical elements can be categorized based on their material and the presence of a coating. Coatings play a crucial role: Identifying the Contaminant Contaminants can be broadly categorized into three types: …
Raytracing in Rust!
I have started a project that requires the use of a raytracer. Basically, I hope to make a library for rendering optical paths using raytracing and simulate the result that one would get by looking through the optical system. Hopefully, I would like to be able to write somewhere that I will have a couple of lenses here and there, give the parameters such as the refractive index and curvatures and diameters and get the resulting image on a focal plane. To do this, I need to start small, and I thought that the way to start small was to …
How do big telescopes look through the atmosphere – Adaptative Optics 101

Continuing my series of post covering my talk from last Christmas about the use of lasers in space and astronomy. The topic today is adaptative optics. I’ll explain the reason why we need it, and how it works in simple terms. Enjoy. No surprise: telescopes are the main tool of astronomers. Since Newton, we have built countless telescopes of various sizes and shapes. And lately, we even send them to space. We have Hubble, the JSWT for the more famous, and a lot of other space telescopes less known. But why sending them to space? After all, space is difficult. …
What is the difference between a regular lamp and a laser? A brief history of Optics and Lasers

So this post and a bunch after this one are from a talk I presented at the end December on the topic of lasers in space and astronomy. The target the audience was members from astronomy groups in the region with some knowledge of optics but not necessarily lasers and the curious people that might be interested but have a physics background from high school. I tried to make it interesting for a wide audience, and I would say that it is accessible to some degree to someone in high school, maybe earlier? Anyway, the goal was to be entertaining, …
Artificial intelligence and the new normal
So that is it. I have been, like many others following what is the biggest paradigm shift of the past hundred years. In my opinion, the true next big step in human history that is being taken right now, as some people might seem to realize it, but also as many others simply ignore. In the early 20th century, the invention of the combustion motor changed everything. From the way people moved to the way people generated electricity, to how they worked. Basically, artificial intelligence is here to do the same, with unforeseen consequences. I have a history of being …
Diffraction patterns in astronomical imaging
The first image from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was uncover a few days ago [1]. This is truely an incredible image, showing the galactic cluster SMACS 0723, which is slowly becoming the de-facto target for newly deployed space telescopes as it was imaged by Hubble, Planck and Chandra before JWST. This image in particular took the JWST 12.5 hours of exposure to be able to see these objects as they are so dim in the sky. The best way to see how much of an achievement this is, is to compare it to the previous picture, taken by …
Digital photonics and laser lightning rods from AKL22
I was at AKL 22 a couple of weeks ago: the international laser technology congress at Aachen, Germany. I was present for the interesting technology conference and the live presentations at Fraunhofer ILT. I have to say that after 2 years of Covid and only being able to assist to virtual conferences if available was a breath of fresh air. Virtual events are nice and you can still learn a few things, but physical events are something else. You are invested in what you hear and there is less distraction than in the office. The best part is that you …
Haidinger’s Brush Or How To See Polarization
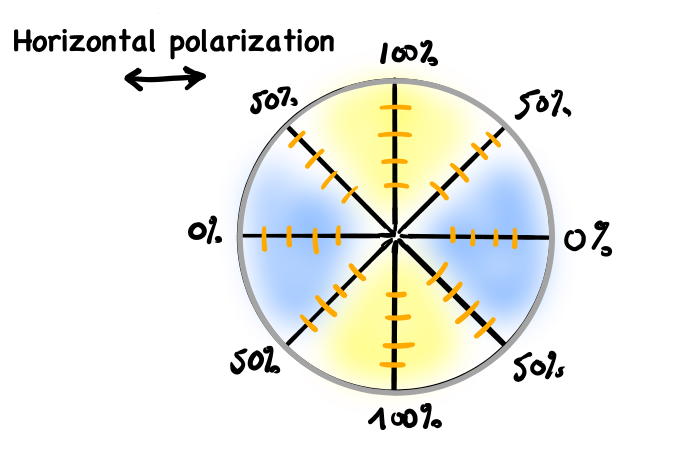
I have always been interested with optics and vision. My path led me to a more technological approach of optics, aka photonics, but I still am fascinated by the process of vision. How the image is formed in the eye, how it is interpreted in the brain and so on. This led me to learn a few things that apparently are not so well known about our own eyes. One of these things is the subject of this post: Haidinger’s brush. To start, it should come to no surprise to you that our eyes are sensitive to colours. We have …
Laser physics: gain medium and population inversion
Continuing the series on lasers. In the first part, I went fast over plenty of concepts and left others on the side because they were not necessary to get a global understanding of lasers. Here, I want to get a little deeper in some specific concepts. I want to talk more in details about the gain medium of a laser and why population inversion is a vital concept. For now, I have been relatively simple on the gain medium characteristics… I have considered a simple material with two atomic energy levels, and I have been assuming that the transition is …